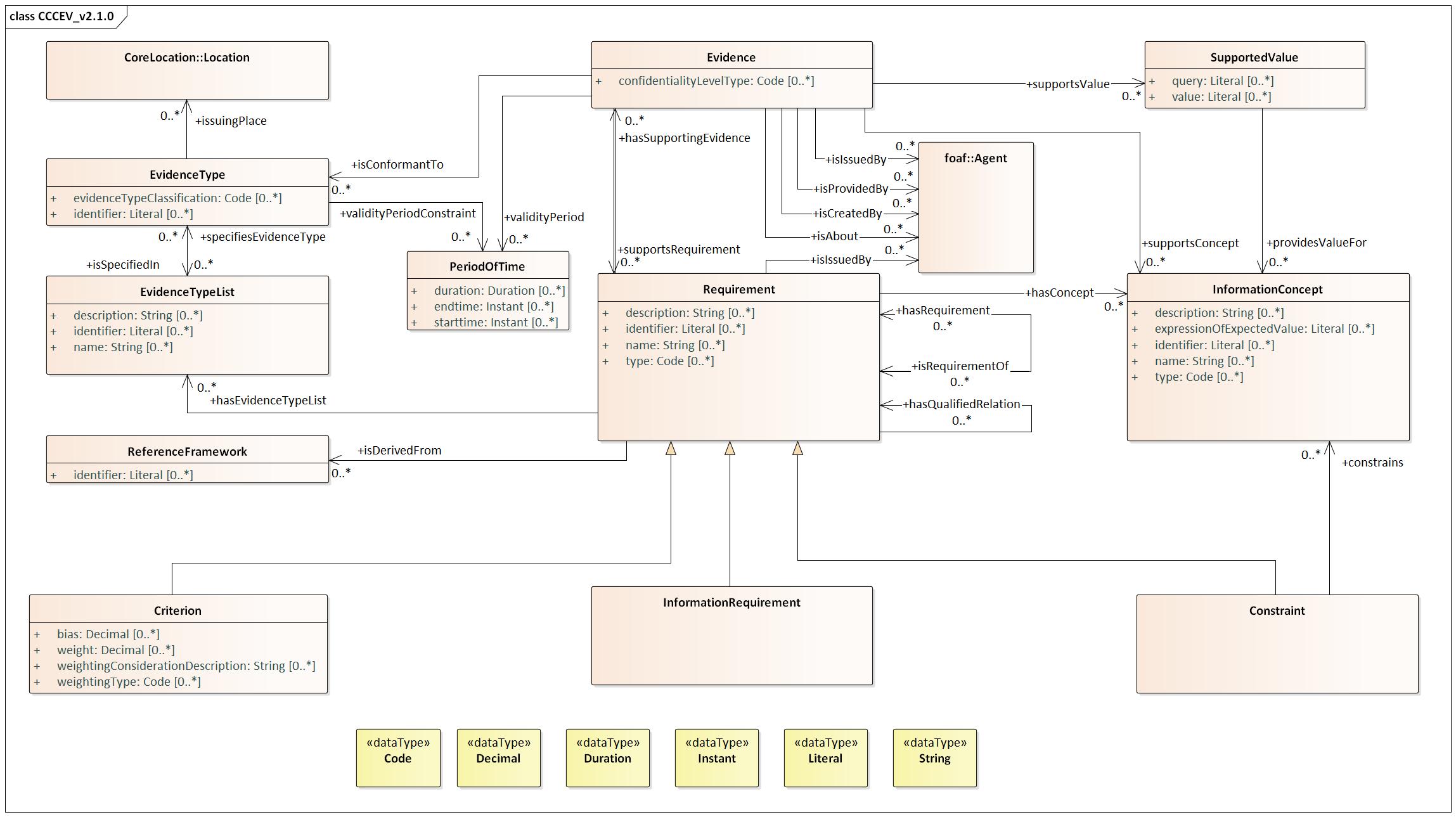
| Agent |
http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/Agent |
|
|
|
| Constraint |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Constraint |
|
constrains |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/constrains |
| Criterion |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Criterion |
|
bias |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/bias |
| Criterion |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Criterion |
|
weight |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/weight |
| Criterion |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Criterion |
|
weighting consideration description |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/weightingConsiderationDescription |
| Criterion |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Criterion |
|
weighting type |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/weightingType |
| Evidence |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Evidence |
|
confidentiality level type |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/confidentialityLevelType |
| Evidence |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Evidence |
|
is about |
http://purl.org/dc/terms/subject |
| Evidence |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Evidence |
|
is conformant to |
http://purl.org/dc/terms/conformsTo |
| Evidence |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Evidence |
|
is created by |
http://purl.org/dc/terms/creator |
| Evidence |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Evidence |
|
is issued by |
http://purl.org/dc/terms/publisher |
| Evidence |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Evidence |
|
is provided by |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/isProvidedBy |
| Evidence |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Evidence |
|
supports concept |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/supportsConcept |
| Evidence |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Evidence |
|
supports requirement |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/supportsRequirement |
| Evidence |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Evidence |
|
supports value |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/supportsValue |
| Evidence |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Evidence |
|
validity period |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/validityPeriod |
| Evidence Type |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/EvidenceType |
|
evidence type classification |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/evidenceTypeClassification |
| Evidence Type |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/EvidenceType |
|
identifier |
http://purl.org/dc/terms/identifier |
| Evidence Type |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/EvidenceType |
|
is specified in |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/isSpecifiedIn |
| Evidence Type |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/EvidenceType |
|
issuing place |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/issuingPlace |
| Evidence Type |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/EvidenceType |
|
validity period constraint |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/validityPeriodConstraint |
| Evidence Type List |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/EvidenceTypeList |
|
description |
http://purl.org/dc/terms/description |
| Evidence Type List |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/EvidenceTypeList |
|
identifier |
http://purl.org/dc/terms/identifier |
| Evidence Type List |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/EvidenceTypeList |
|
name |
http://www.w3.org/2004/02/skos/core#prefLabel |
| Evidence Type List |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/EvidenceTypeList |
|
specifies evidence type |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/specifiesEvidenceType |
| Information Concept |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/InformationConcept |
|
description |
http://purl.org/dc/terms/description |
| Information Concept |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/InformationConcept |
|
expression of expected value |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/expressionOfExpectedValue |
| Information Concept |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/InformationConcept |
|
identifier |
http://purl.org/dc/terms/identifier |
| Information Concept |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/InformationConcept |
|
name |
http://www.w3.org/2004/02/skos/core#prefLabel |
| Information Concept |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/InformationConcept |
|
type |
http://purl.org/dc/terms/type |
| Information Requirement |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/InformationRequirement |
|
|
|
| Location |
http://purl.org/dc/terms/Location |
|
|
|
| Period of Time |
http://www.w3.org/2006/time#ProperInterval |
|
duration |
http://www.w3.org/2006/time#hasXSDDuration |
| Period of Time |
http://www.w3.org/2006/time#ProperInterval |
|
endtime |
http://www.w3.org/2006/time#hasEnd |
| Period of Time |
http://www.w3.org/2006/time#ProperInterval |
|
starttime |
http://www.w3.org/2006/time#hasBeginning |
| Reference Framework |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/ReferenceFramework |
|
identifier |
http://purl.org/dc/terms/identifier |
| Requirement |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Requirement |
|
description |
http://purl.org/dc/terms/description |
| Requirement |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Requirement |
|
has concept |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/hasConcept |
| Requirement |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Requirement |
|
has evidence type list |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/hasEvidenceTypeList |
| Requirement |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Requirement |
|
has qualified relation |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/hasQualifiedRelation |
| Requirement |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Requirement |
|
has requirement |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/hasRequirement |
| Requirement |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Requirement |
|
has supporting evidence |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/hasSupportingEvidence |
| Requirement |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Requirement |
|
identifier |
http://purl.org/dc/terms/identifier |
| Requirement |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Requirement |
|
is derived from |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/isDerivedFrom |
| Requirement |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Requirement |
|
is issued by |
http://purl.org/dc/terms/publisher |
| Requirement |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Requirement |
|
is requirement of |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/isRequirementOf |
| Requirement |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Requirement |
|
name |
http://www.w3.org/2004/02/skos/core#prefLabel |
| Requirement |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/Requirement |
|
type |
http://purl.org/dc/terms/type |
| Supported Value |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/SupportedValue |
|
provides value for |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/providesValueFor |
| Supported Value |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/SupportedValue |
|
query |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/query |
| Supported Value |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/SupportedValue |
|
value |
http://data.europa.eu/m8g/value |
![[o]](html/callout.png)