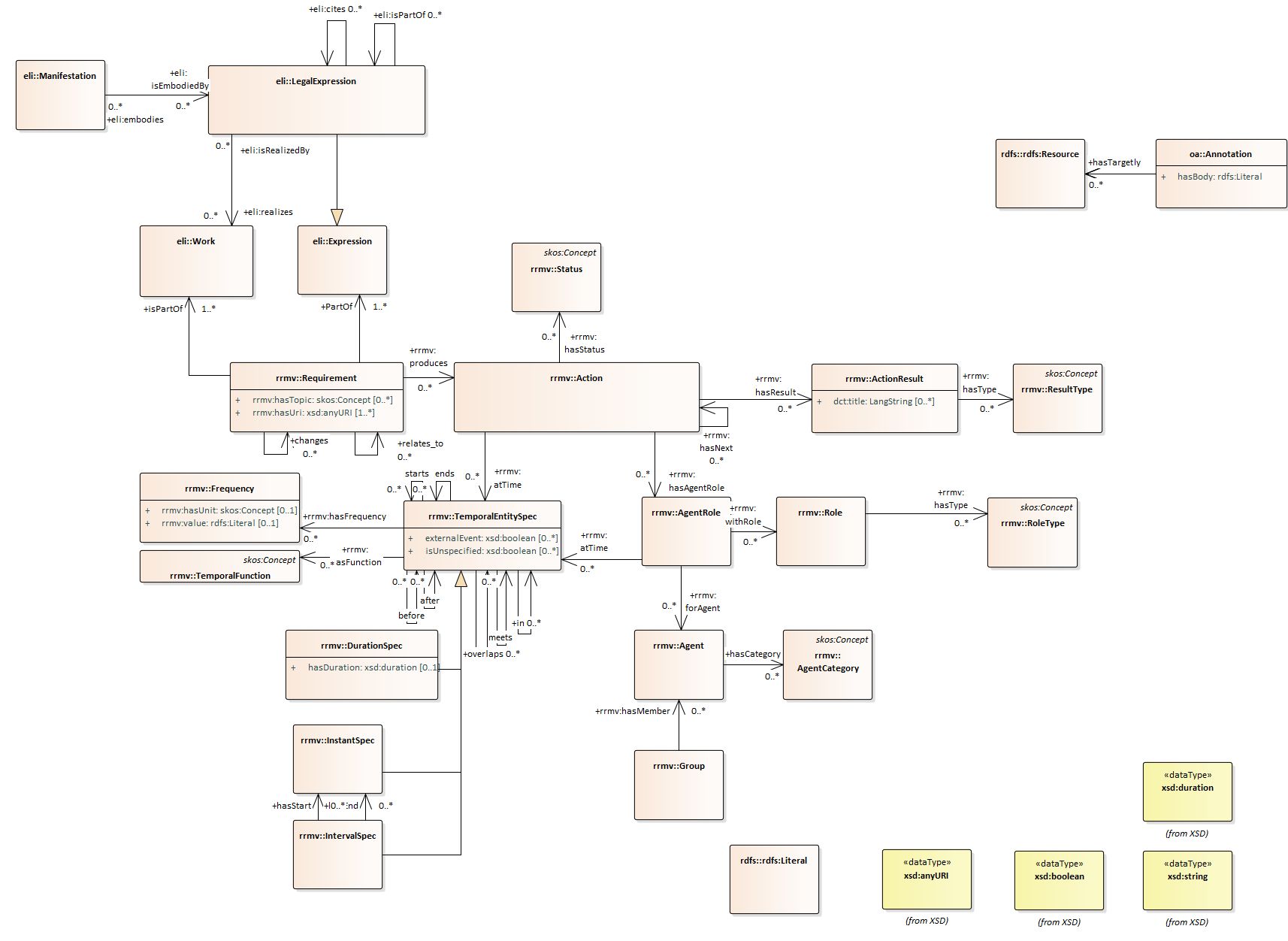
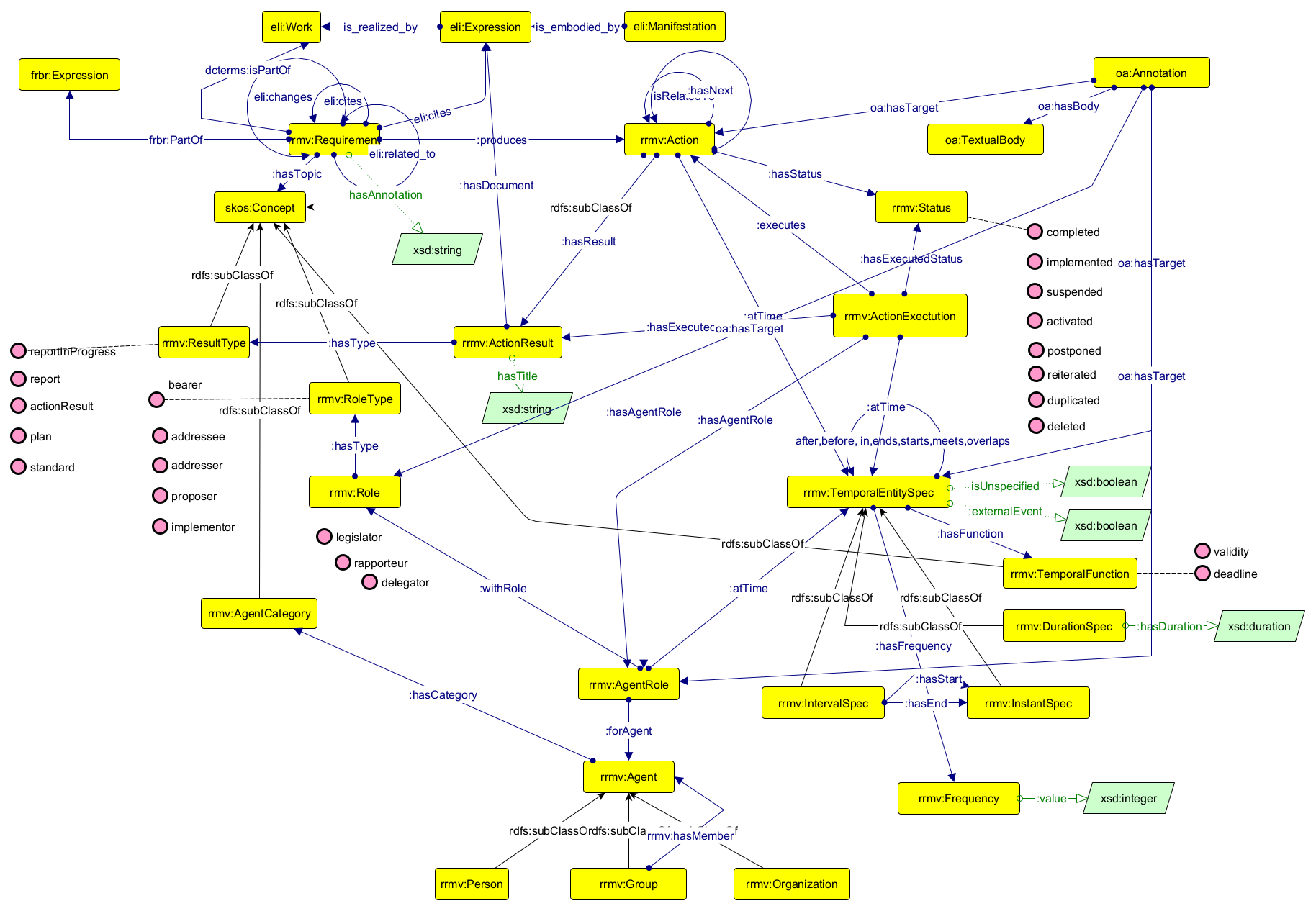
| Action |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#Action |
|
at time |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#atTime |
| Action |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#Action |
|
has agent role |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#hasAgentRole |
| Action |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#Action |
|
has next |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#hasNext |
| Action |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#Action |
|
has result |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#hasResult |
| Action |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#Action |
|
has status |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#hasStatus |
| Action Result |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#ActionResult |
|
has title |
http://purl.org/dc/terms/title |
| Action Result |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#ActionResult |
|
has type |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#hasType |
| Agent |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#Agent |
|
has category |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#hasCategory |
| Agent Category |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#AgentCategory |
|
|
|
| Agent Role |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#AgentRole |
|
at time |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#atTime |
| Agent Role |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#AgentRole |
|
for agent |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#forAgent |
| Agent Role |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#AgentRole |
|
with role |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#withRole |
| Annotation |
http://www.w3.org/ns/oa#Annotation |
|
body value |
http://www.w3.org/ns/oa#bodyValue |
| Annotation |
http://www.w3.org/ns/oa#Annotation |
|
has body |
http://www.w3.org/ns/oa#hasBody |
| Annotation |
http://www.w3.org/ns/oa#Annotation |
|
has target |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#hasTarget |
| Concept |
http://www.w3.org/2004/02/skos/core#Concept |
|
preferred label |
http://www.w3.org/2004/02/skos/core#prefLabel |
| Duration Temporal Entity Specification |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#DurationSpec |
|
has duration |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#hasDuration |
| Expression |
http://data.europa.eu/eli/ontology#Expression |
|
|
|
| Frequency |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#Frequency |
|
has unit |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#hasUnit |
| Frequency |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#Frequency |
|
value |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#value |
| Group |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#Group |
|
has member |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#rrmv:hasMember |
| Instant Temporal Entity Specification |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#InstantSpec |
|
|
|
| Interval Temporal Entity Specification |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#IntervalSpec |
|
has end |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#hasEnd |
| Interval Temporal Entity Specification |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#IntervalSpec |
|
has start |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#hasStart |
| Legal Expression |
http://data.europa.eu/eli/ontology#LegalExpression |
|
cites |
http://data.europa.eu/eli/ontology#cites |
| Legal Expression |
http://data.europa.eu/eli/ontology#LegalExpression |
|
embodies |
http://data.europa.eu/eli/ontology#embodies |
| Legal Expression |
http://data.europa.eu/eli/ontology#LegalExpression |
|
is part of |
http://data.europa.eu/eli/ontology#is_part_of |
| Legal Expression |
http://data.europa.eu/eli/ontology#LegalExpression |
|
realizes |
http://data.europa.eu/eli/ontology#realizes |
| Literal |
http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#Literal |
|
|
|
| Manifestation |
http://data.europa.eu/eli/ontology#Manifestation |
|
is embodied by |
http://data.europa.eu/eli/ontology#is_embodied_by |
| Requirement |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#Requirement |
|
changes |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#changes |
| Requirement |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#Requirement |
|
has topic |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#hasTopic |
| Requirement |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#Requirement |
|
has URI |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#hasURI |
| Requirement |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#Requirement |
|
is part of |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#isPartOf |
| Requirement |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#Requirement |
|
part of |
https://www.iflastandards.info/fr/frbr/frbroo#R8i |
| Requirement |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#Requirement |
|
produces |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#produces |
| Requirement |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#Requirement |
|
related to |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#related_to |
| Resource |
http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#Resource |
|
|
|
| Result Type |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#ResultType |
|
|
|
| Role |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#Role |
|
has type |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#hasType |
| Role Type |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#RoleType |
|
|
|
| Status |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#Status |
|
|
|
| Temporal Entity Specification |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#TemporalEntitySpec |
|
after |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#after |
| Temporal Entity Specification |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#TemporalEntitySpec |
|
before |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#before |
| Temporal Entity Specification |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#TemporalEntitySpec |
|
ends |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#ends |
| Temporal Entity Specification |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#TemporalEntitySpec |
|
external event |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#externalEvent |
| Temporal Entity Specification |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#TemporalEntitySpec |
|
has frequency |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#hasFrequency |
| Temporal Entity Specification |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#TemporalEntitySpec |
|
has function |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#hasFunction |
| Temporal Entity Specification |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#TemporalEntitySpec |
|
in |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#in |
| Temporal Entity Specification |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#TemporalEntitySpec |
|
is unspecified |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#isUnspecified |
| Temporal Entity Specification |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#TemporalEntitySpec |
|
meets |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#meets |
| Temporal Entity Specification |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#TemporalEntitySpec |
|
overlaps |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#overlaps |
| Temporal Entity Specification |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#TemporalEntitySpec |
|
starts |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#starts |
| Temporal Function |
http://data.europa.eu/2qy/rrmv#TemporalFunction |
|
|
|
| Work |
http://data.europa.eu/eli/ontology#Work |
|
is realized by |
http://data.europa.eu/eli/ontology#is_realized_by |